To service the rear brakes on a 2019 Hyundai Santa Fe, you must engage the EPB service mode. This can be done using a compatible OBDII scan tool with the brake servicing feature. Alternatively, a manual method involves disconnecting the negative battery cable, unplugging the parking brake actuator, and manually retracting the caliper.
The Electric Parking Brake Functionality
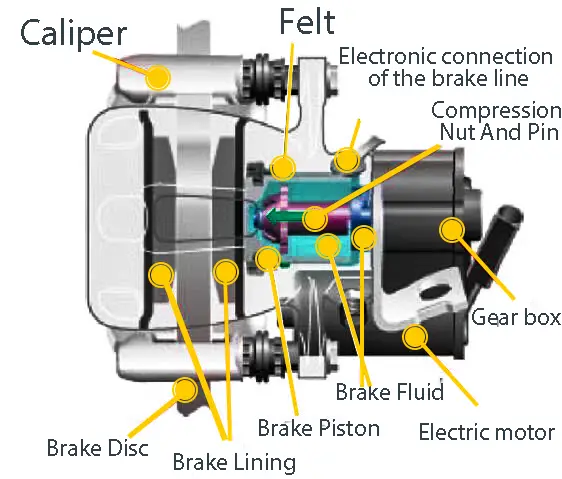
How does the electric parking brake system work?
The electric parking brake (EPB) system is a modern replacement for the traditional mechanical parking brake. It functions by using an electronic control unit (ECU) and actuators to apply the brakes.
When the driver activates the EPB via a button, the ECU sends a signal to the actuators, which then apply the brake pads to the rear wheels. There are two main types of EPB systems: the cable puller system and the caliper integrated system.
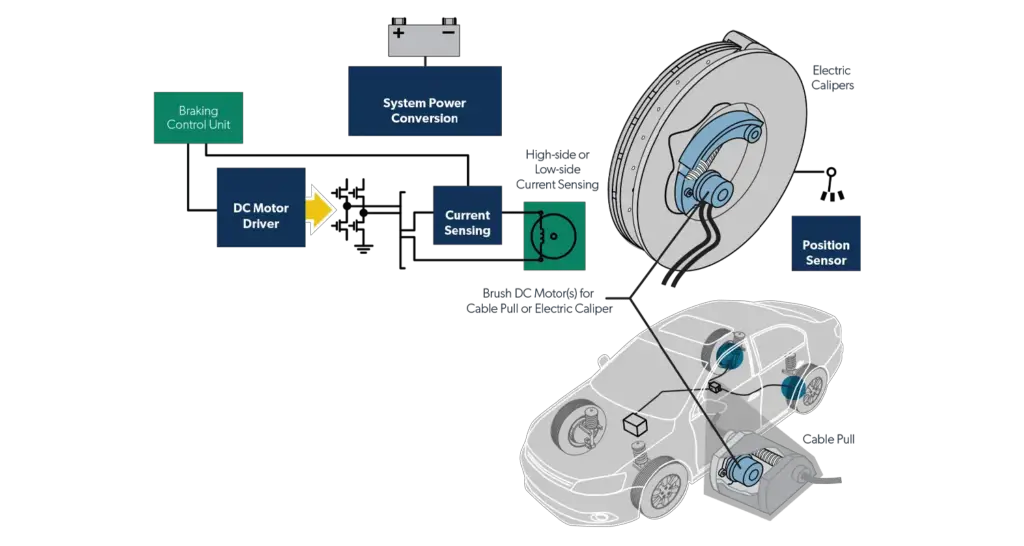
In the cable puller system, a motor pulls a cable that applies the brakes, similar to traditional handbrakes but operated electrically. In the caliper integrated system, an electric motor within each brake caliper directly applies the brake pads to the discs.
This system is integrated with other vehicle systems through the Controller Area Network (CAN), allowing for coordinated control with features like the Antilock Braking System (ABS).
Benefits of using an electric parking brake

The electric parking brake offers several advantages over traditional mechanical systems:
- Ease of Use: The EPB is activated by a simple push of a button, making it more convenient and user-friendly.
- Safety Features: It includes safety enhancements such as automatic engagement when the vehicle is parked on an incline or when the car is turned off. This prevents the vehicle from rolling unintentionally.
- Space Saving: The absence of a traditional lever frees up space in the vehicle’s cabin, allowing for more ergonomic and aesthetic design options.
- Precision: EPBs provide greater precision in applying braking force, which is particularly useful on steep slopes or in emergency situations.
- Maintenance: While EPBs might require less frequent maintenance, the maintenance needed is more specialized due to the electronic components involved.
Enhancing safety and convenience for Santa Fe drivers
For Hyundai Santa Fe models equipped with an electric parking brake, the system enhances both safety and convenience:
- Automatic Functionality: The EPB in the Santa Fe can automatically engage or disengage based on certain conditions, such as when the vehicle is parked on a slope or when the driver begins to accelerate. This feature adds a layer of safety by preventing the vehicle from rolling unintentionally.
- Integration with Advanced Safety Systems: In the Santa Fe, the EPB works in conjunction with other safety systems like Hill Start Assist, which temporarily holds the brakes to prevent the car from rolling back on a slope when moving from a stop.
Releasing the Rear Electric Parking Brake for Service

Step-by-Step Instructions for Releasing the Electric Parking Brake
When servicing the rear brakes on a vehicle equipped with an electric parking brake (EPB), it is crucial to properly release the EPB before beginning any work. The process for releasing the EPB can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, but generally involves the following steps:
- Ensure the vehicle is on a level surface and the ignition is turned on.
- Apply the foot brake to ensure the vehicle does not move during the process.
- Depending on the vehicle, you may need to use a scan tool to put the EPB into service mode. This is often done through the vehicle’s diagnostic port and requires selecting the appropriate function on the scan tool.
- For some vehicles, there may be a manual procedure involving a sequence of actions such as pressing certain buttons or using the infotainment screen.
- Once the EPB is in service mode, the brake calipers can be safely worked on without the EPB applying force to the brake pads.
Different Methods to Disengage the EPB
There are several methods to disengage the EPB, and the appropriate method depends on the specific vehicle and tools available:
- Using a Scan Tool: This is the most common and recommended method. A scan tool can communicate with the vehicle’s electronic systems to retract the parking brake mechanism inside the caliper, often referred to as service mode.
- Manual Procedures: Some vehicles have a built-in manual procedure that can be performed without a scan tool. This may involve a combination of button presses or other actions.
- Mechanical Tools: In some cases, mechanical tools like a caliper wind back tool can be used to manually retract the caliper pistons. However, this should be done with caution to avoid damaging the EPB system.
- Direct Power Supply: A more unconventional method involves applying a direct power supply to the parking brake motor to retract it. This method should be used with caution and only by those who understand the risks and have the technical knowledge to avoid damaging the vehicle’s electrical system.
The Importance of Properly Releasing the EPB
Properly releasing the EPB is essential for several reasons:
- Avoiding Damage: Attempting to service the brakes without disengaging the EPB can result in damage to the brake calipers, actuators, or other components of the brake system.
- Safety: Working on the brakes with the EPB engaged can be dangerous, as it may cause the vehicle to move unexpectedly if the EPB is accidentally activated.
- Maintaining System Integrity: Properly releasing the EPB ensures that the system’s integrity is maintained, and the EPB will function correctly when reactivated after service.
Steps to Change Rear Brake Pads with EPB with Tools and Techniques
Changing the rear brake pads on a vehicle equipped with an Electric Parking Brake (EPB) requires specific steps to ensure that the EPB system is not damaged during the process. Here are the general steps, tools, and techniques based on the provided sources:
Tools Required:
- A standard brake tool or a piston compression tool
- A scan tool or OBD tool (optional, depending on the vehicle)
- Allen keys or sockets (specific sizes may vary by vehicle)
- Torx sockets (specific sizes may vary by vehicle)
- A wrench or impact wrench
- A pry bar (if necessary)
- A jack and jack stands
- Wheel chocks
Techniques and Steps:
Prepare the Vehicle:
- Ensure the vehicle is on a level surface and safely raised off the ground.
- Use wheel chocks to secure the vehicle.
- Release the EPB either by using the vehicle’s manual release procedure or by putting the vehicle into service mode using a scan tool or OBD tool.
Remove the EPB Actuator (if applicable):
- Some vehicles require the removal of the EPB actuator to access the spindle head that needs to be manually retracted before servicing the brake.
- Disconnect the electrical connector and remove any bolts securing the actuator to the caliper.
- Carefully wiggle the actuator housing to remove it from the caliper.
Retract the Piston:
- For vehicles that require it, manually retract the spindle head using a Torx socket.
- Use a piston compression tool or similar device to push the caliper piston back into the caliper to make room for new brake pads.
- Ensure that the piston boot is not protruding past the piston surface.
Replace the Brake Pads:
- Remove the old brake pads and fit the new ones into place.
- If the caliper was removed, reposition it over the new pads and secure it with the appropriate bolts.
Reassemble and Test:
- If an actuator was removed, align and reinstall it onto the caliper.
- Ensure all components are properly tightened and secured.
- Lower the vehicle and disengage any service mode if it was activated.
- Pump the brake pedal to ensure the new pads are seated and the piston is correctly adjusted.
- Perform a function test of the EPB to ensure it is working correctly.
Final Checks:
- Go for a test drive to ensure the brakes are functioning properly and the EPB is engaging and releasing as expected.
Important Considerations:
- Always refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions related to the make and model.
- Some vehicles allow for manual retraction of the EPB without the use of a scan tool, while others strictly require the use of a diagnostic system to avoid damaging the EPB system[1][2][6].
- It is crucial not to force any components and to ensure proper alignment during reassembly to avoid issues with the EPB system.
Tips and Advice for Rear Brake Pad Replacement with EPB

Preparing for the Rear Brake Pad Replacement
- Ensure Vehicle Stability: Before starting, make sure the vehicle is parked on a level surface and securely supported by jack stands.
- Disengage the EPB: Use a scan tool or vehicle-specific procedure to put the EPB into service mode. This is crucial to prevent damage to the brake system[.
- Check System Voltage: Maintain adequate battery voltage throughout the process, as low voltage can affect the EPB’s functionality.
- Gather Necessary Tools: Have all required tools at hand, including a brake caliper tool, Torx or Allen sockets, and a piston compressor if needed.
Common Pitfalls and Mistakes to Avoid
- Forcing the Piston: Never force the piston back into the caliper without first ensuring the EPB is in service mode. Forcing it can damage the mechanism.
- Incorrect Tool Use: Using the wrong tools can damage the components. Ensure you’re using the correct tools for your vehicle model.
- Neglecting EPB Actuator: If your vehicle requires removal of the EPB actuator, handle it carefully and ensure it is correctly repositioned and recalibrated during reassembly.
- Skipping Steps: Do not skip any steps in the EPB disengagement process. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to avoid system errors.
Ensuring Proper Alignment and Functionality
- Correct Pad Installation: Ensure that the brake pads are installed correctly. Incorrect installation can lead to reduced braking efficiency and premature wear.
- Caliper Alignment: Properly align the caliper and make sure it is not binding or misaligned, which could cause uneven pad wear and poor braking performance.
- System Calibration: After replacing the pads and reassembling the brakes, recalibrate the EPB system using a diagnostic tool to ensure it functions correctly.
- Test Drive: Always perform a test drive in a safe area to ensure the brakes are functioning properly and the EPB engages and releases as expected.
Exploring the Hyundai Santa Fe Specs for Other Model Years
Different Hyundai Santa Fe Models Over the Years
- First Generation (2001-2006): Introduced as Hyundai’s first SUV with options like a 2.4-liter four-cylinder or a more powerful 2.7-liter V6 engine.
- Second Generation (2007-2012): Featured increased size for more interior space, updated safety systems, and engine options including a new 2.2-liter diesel and a 2.7-liter V6.
- Third Generation (2013-2018): Introduced the Santa Fe Sport model and included more modern safety features and engine options like a turbocharged 2.0-liter four-cylinder.
- Fourth Generation (2019-2023): Marked by a redesign with updated tech and safety features, discontinuing the 3.3-liter V6 and introducing more efficient engine options.
- Fifth Generation (2023-Present): Features a more boxy design, improved aerodynamics, and updated powertrains including hybrid options.
Choosing the Right Model Year
- Best Years: 2006, 2020, and 2023 are noted for fewer complaints and recalls.
- Years to Avoid: 2001-2003, 2007, 2012, and 2017 due to higher reports of issues and recalls.
Putting Your Faith in Hyundai
- Hyundai has consistently improved the Santa Fe’s design, safety, and technology over the years, making newer models generally more reliable and feature-rich.
- The brand’s commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction is evident in the progressive enhancements seen across different generations.
Optimizing EPB Service Mode for 2019 Hyundai Santa Fe
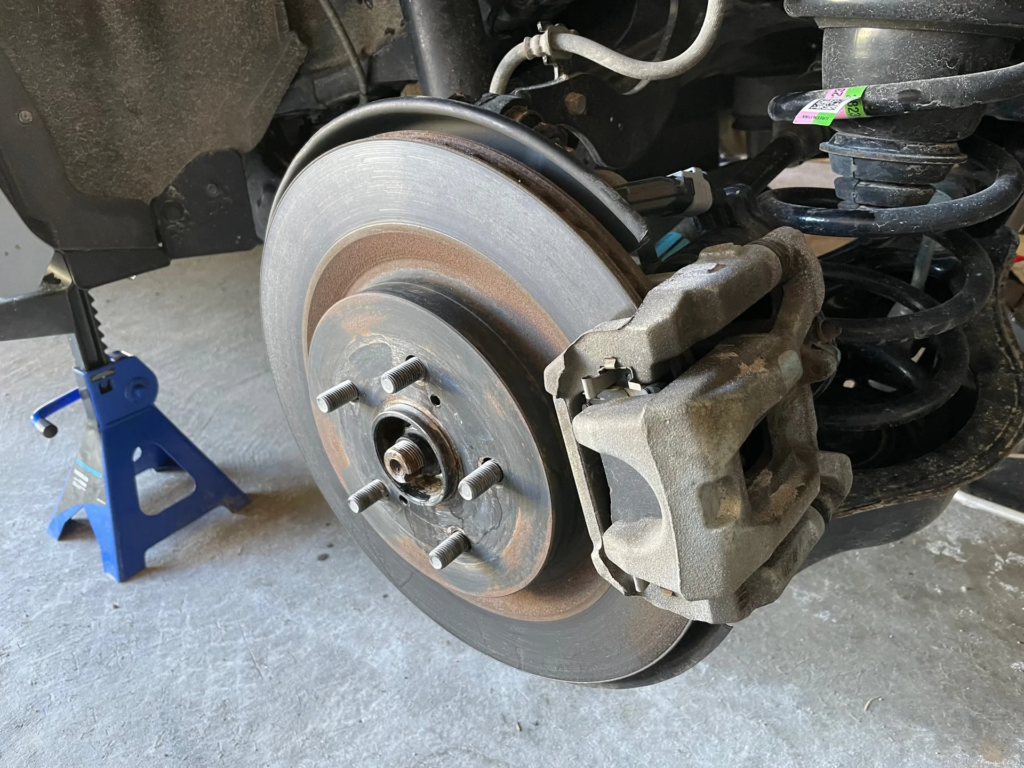

Maximize the Benefits of EPB Service Mode
To maximize the benefits of the Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) service mode in the 2019 Hyundai Santa Fe, follow these steps:
- Use a Compatible Scan Tool: Ensure you have a scan tool that supports the EPB service mode for Hyundai vehicles. This tool is essential for safely retracting the brake calipers when replacing the brake pads.
- Engage Service Mode Before Maintenance: Before starting any brake maintenance, activate the EPB service mode using the scan tool. This will retract the brake calipers and prevent any mechanical strain or damage during the pad replacement.
- Follow Specific Instructions: Each vehicle model may have slightly different requirements for engaging and disengaging the EPB service mode. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for detailed instructions specific to the 2019 Hyundai Santa Fe.
- Check for Software Updates: Regularly update the software of your scan tool to ensure compatibility and functionality with the latest vehicle models and their electronic systems.
Importance of Regular EPB System Checks and Maintenance
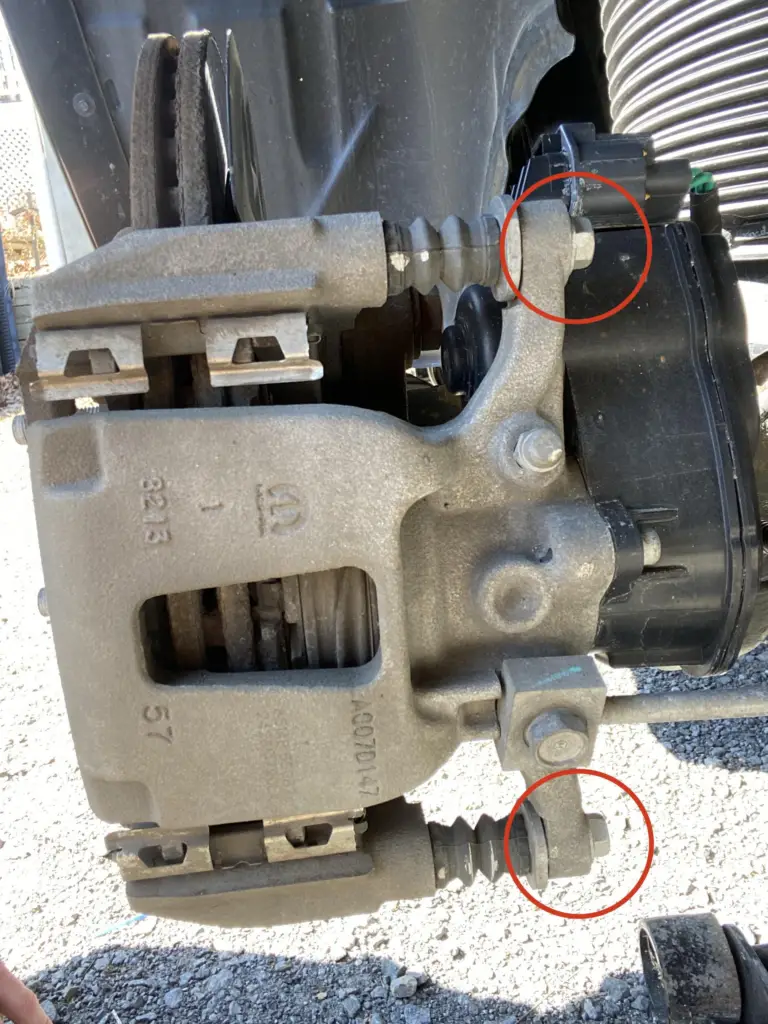
Regular checks and maintenance of the EPB system are crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: The EPB system holds the vehicle stationary on slopes and during parking. Regular maintenance ensures reliable operation, preventing unintentional vehicle movement.
- Preventive Care: Routine inspections can identify potential issues early, such as wear or electronic faults, before they lead to more significant problems or failures.
- System Longevity: Maintaining the EPB system, including software updates and mechanical checks, can extend the life of the components and reduce the likelihood of costly repairs.
- Compliance with Warranty Requirements: Regular maintenance may be necessary to comply with warranty terms, ensuring that any repairs or replacements are covered by the manufacturer.
FAQ
Can I perform rear brake pad replacement without using EPB service mode?
No, it is not recommended to perform rear brake pad replacement without first putting the EPB into service mode. Engaging service mode retracts the brake calipers electronically and prevents potential damage to the EPB system. Some vehicles may allow manual retraction, but this should be done with caution and proper knowledge of the vehicle’s brake system.
How often should I change my Hyundai Santa Fe’s rear brake pads?
The frequency of changing your Hyundai Santa Fe’s rear brake pads can vary based on driving habits and conditions, but experts generally recommend replacing brake pads every 30,000 to 35,000 miles[10]. Always look for signs of wear, such as a decrease in braking performance or unusual noises when braking.
Are there any specific tools required for rear brake pad replacement with EPB?
Yes, specific tools are required for rear brake pad replacement with EPB. These may include a brake caliper tool, a piston compressor, and possibly a diagnostic scan tool to engage and disengage the EPB service mode. The exact tools can vary depending on the vehicle model and the EPB system type.
Can I reset the EPB system myself after replacing the rear brake pads?
Yes, you can reset the EPB system yourself after replacing the rear brake pads, but it requires following the correct procedure for your specific vehicle model. Some vehicles may allow a manual reset, while others may require the use of a diagnostic scan tool to recalibrate the system.
What should I do if I encounter any issues while performing rear brake service on my Hyundai Santa Fe?
If you encounter any issues while performing rear brake service on your Hyundai Santa Fe, it is important to stop and assess the situation. If the EPB system is not functioning properly or if there are warning lights on the dashboard, it may be necessary to consult the vehicle’s service manual, seek professional assistance, or use a diagnostic scan tool to troubleshoot and resolve the issue.